Monday, December 15, 2014
Connections in SIM card

I/O -Input/Output
Vcc -Common collector voltage
Vpp -Peak to peak voltage?
GND -Ground or earth...
For more details click here
Tuesday, December 9, 2014
WHY TO VISIT TEMPLES ???
Believe in science not the crap....

Scientific Reasons behind visiting temples :

Scientific Reasons behind visiting temples :
There are
thousands of temples all over India in different size, shape and
locations but not all of them are considered to be built the Vedic way.
Generally, a temple should be located at a place where earth's magnetic
wave path passes through densely. It can be in the outskirts of a
town/village or city, or in middle of the dwelling place, or on a
hilltop. The essence of visiting a temple is discussed here.
Now, these temples are located strategically at a place where the positive energy is abundantly available from the magnetic and electric wave distributions of north/south pole thrust. The main idol is placed in the core center of the temple, known as "*Garbhagriha*" or *Moolasthanam*. In fact, the temple structure is built after the idol has been placed. This *Moolasthanam* is where earth’s magnetic waves are found to be maximum. We know that there are some copper plates, inscribed with Vedic scripts, buried beneath the Main Idol. What are they really? No, they are not God’s / priests’ flash cards when they forget the *shlokas*. The copper plate absorbs earth’s magnetic waves and radiates it to the surroundings. Thus a person regularly visiting a temple and walking clockwise around the Main Idol receives the beamed magnetic waves and his body absorbs it. This is a very slow process and a regular visit will let him absorb more of this positive energy. Scientifically, it is the positive energy that we all require to have a healthy life.
Further, the Sanctum is closed on three sides. This increases the effect of all energies.
The lamp that is lit radiates heat energy and also provides light inside the sanctum to the priests or *poojaris* performing the pooja. The ringing of the bells and the chanting of prayers takes a worshipper into trance, thus not letting his mind waver. When done in groups, this helps people forget personal problems for a while and relieve their stress. The fragrance from the flowers, the burning of camphor give out the chemical energy further aiding in a different good aura. The effect of all these energies is supplemented by the positive energy from the idol, the copper plates and utensils in the *Moolasthan*am / *Garbagraham*. *Theertham*, the “holy” water used during the pooja to wash the idol is not plain water cleaning the dust off an idol. It is a concoction of Cardamom,*Karpura* (Benzoin), zaffron / saffron, *Tulsi* (Holy Basil), Clove, etc...Washing the idol is to charge the water with the magnetic radiations thus increasing its medicinal values. Three spoons of this holy water is distributed to devotees. Again, this water is mainly a source of magneto-therapy. Besides, the clove essence protects one from tooth decay, the saffron & *Tulsi* leafs protects one from common cold and cough, cardamom and *Pachha Karpuram* (benzoin), act as mouth fresheners. It is proved that *Theertham* is a very good blood purifier, as it is highly energized. Hence it is given as *prasadam* to the devotees. This way, one can claim to remain healthy by regularly visiting the Temples. This is why our elders used to suggest us to offer prayers at the temple so that you will be cured of many ailments. They were not always superstitious. Yes, in a few cases they did go overboard when due to ignorance they hoped many serious diseases could be cured at temples by deities.
When people go to a temple for the *Deepaaraadhana*, and when the doors open up, the positive energy gushes out onto the persons who are there. The water that is sprinkled onto the assemblages passes on the energy to all. This also explains why men are not allowed to wear shirts at a few temples and women are requested to wear more ornaments during temple visits. It is through these jewels (metal) that positive energy is absorbed by the women. Also, it is a practice to leave newly purchased jewels at an idol’s feet and then wear them with the idol’s blessings. This act is now justified after reading this article. This act of “seeking divine blessings” before using any new article, like books or pens or automobiles may have stemmed from this through mere observation.
Energy lost in a day’s work is regained through a temple visit and one is refreshed slightly. The positive energy that is spread out in the entire temple and especially around where the main idol is placed, are simply absorbed by one's body and mind. Did you know, every Vaishnava(Vishnu devotees), “must” visit a Vishnu temple twice every day in their location. Our practices are NOT some hard and fast rules framed by 1 man and his followers or God’s words in somebody’s dreams. All the rituals, all the practices are, in reality, well researched, studied and scientifically backed thesis which form the ways of nature to lead a good healthy life.
The scientific and research part of the practices are well camouflaged as “elder’s instructions” or “granny’s teaching’s” which should be obeyed as a mark of respect so as to once again, avoid stress to the mediocre brains.
Now, these temples are located strategically at a place where the positive energy is abundantly available from the magnetic and electric wave distributions of north/south pole thrust. The main idol is placed in the core center of the temple, known as "*Garbhagriha*" or *Moolasthanam*. In fact, the temple structure is built after the idol has been placed. This *Moolasthanam* is where earth’s magnetic waves are found to be maximum. We know that there are some copper plates, inscribed with Vedic scripts, buried beneath the Main Idol. What are they really? No, they are not God’s / priests’ flash cards when they forget the *shlokas*. The copper plate absorbs earth’s magnetic waves and radiates it to the surroundings. Thus a person regularly visiting a temple and walking clockwise around the Main Idol receives the beamed magnetic waves and his body absorbs it. This is a very slow process and a regular visit will let him absorb more of this positive energy. Scientifically, it is the positive energy that we all require to have a healthy life.
Further, the Sanctum is closed on three sides. This increases the effect of all energies.
The lamp that is lit radiates heat energy and also provides light inside the sanctum to the priests or *poojaris* performing the pooja. The ringing of the bells and the chanting of prayers takes a worshipper into trance, thus not letting his mind waver. When done in groups, this helps people forget personal problems for a while and relieve their stress. The fragrance from the flowers, the burning of camphor give out the chemical energy further aiding in a different good aura. The effect of all these energies is supplemented by the positive energy from the idol, the copper plates and utensils in the *Moolasthan*am / *Garbagraham*. *Theertham*, the “holy” water used during the pooja to wash the idol is not plain water cleaning the dust off an idol. It is a concoction of Cardamom,*Karpura* (Benzoin), zaffron / saffron, *Tulsi* (Holy Basil), Clove, etc...Washing the idol is to charge the water with the magnetic radiations thus increasing its medicinal values. Three spoons of this holy water is distributed to devotees. Again, this water is mainly a source of magneto-therapy. Besides, the clove essence protects one from tooth decay, the saffron & *Tulsi* leafs protects one from common cold and cough, cardamom and *Pachha Karpuram* (benzoin), act as mouth fresheners. It is proved that *Theertham* is a very good blood purifier, as it is highly energized. Hence it is given as *prasadam* to the devotees. This way, one can claim to remain healthy by regularly visiting the Temples. This is why our elders used to suggest us to offer prayers at the temple so that you will be cured of many ailments. They were not always superstitious. Yes, in a few cases they did go overboard when due to ignorance they hoped many serious diseases could be cured at temples by deities.
When people go to a temple for the *Deepaaraadhana*, and when the doors open up, the positive energy gushes out onto the persons who are there. The water that is sprinkled onto the assemblages passes on the energy to all. This also explains why men are not allowed to wear shirts at a few temples and women are requested to wear more ornaments during temple visits. It is through these jewels (metal) that positive energy is absorbed by the women. Also, it is a practice to leave newly purchased jewels at an idol’s feet and then wear them with the idol’s blessings. This act is now justified after reading this article. This act of “seeking divine blessings” before using any new article, like books or pens or automobiles may have stemmed from this through mere observation.
Energy lost in a day’s work is regained through a temple visit and one is refreshed slightly. The positive energy that is spread out in the entire temple and especially around where the main idol is placed, are simply absorbed by one's body and mind. Did you know, every Vaishnava(Vishnu devotees), “must” visit a Vishnu temple twice every day in their location. Our practices are NOT some hard and fast rules framed by 1 man and his followers or God’s words in somebody’s dreams. All the rituals, all the practices are, in reality, well researched, studied and scientifically backed thesis which form the ways of nature to lead a good healthy life.
The scientific and research part of the practices are well camouflaged as “elder’s instructions” or “granny’s teaching’s” which should be obeyed as a mark of respect so as to once again, avoid stress to the mediocre brains.
Tuesday, October 14, 2014
GATE 2015 Mock Test for practicing Online GATE pattern
Everybody is afraid of new pattern of GATE exam, this post may help you to give exam flawlessly.
GATE 2015 Mock Test- Candidates can perform better by using the GATE 2015 Mock Test for Practice to prepare better for the GATE 2015 Online Tests which is introduced newly. Candidates can avail Mock Tests for GATE 2015 Papers individually as soon as they are announced by IIT Kanpur the organizing institute for GATE 2015. In the meantime, candidates can use the GATE 2014 mock tests below (provided by IIT Kharagpur) to practice the online GATE test papers.Candidates can avail the mock test by clicking on the tests provided for each paper below on this page.

How to use to GATE 2015 Mock Test for Practice:
- Candidates must use only Internet Explorer 7.0/8.0/9.0 on Windows XP/7.
- To go to the Log in page, candidates have to click the given link.
- The Login and password fields will be disabled for the each of the GATE 2015 Mock Test. so candidates can just click and start the test.
- Candidates must note that the GATE 2015 Mock Test for Practice will not note the responses entered by candidates.
- Therefore scores for the GATE 2015 Mock Tests will not be generated
- Candidates can terminate the GATE 2015 Mock Test for Practice anytime they wish to
Check the GATE 2014 Mock Test for Practice below:
S.No GATE 2014 Paper GATE 2014 Paper Code Link to start GATE 2014 Mock test 1Mock Test - Aerospace Engineering AEClick here to start the demo test2Mock Test - Agricultural Engineering AGClick here to start the demo test3Mock Test - Architecture and Planning ARClick here to start the demo test4Mock Test - Biotechnology BTClick here to start the demo test5Mock Test - Civil Engineering CEClick here to start the demo test6Mock Test - Chemical Engineering CHClick here to start the demo test7Mock Test - Computer Science and Information Technology CSClick here to start the demo test8Mock Test - Chemistry CYClick here to start the demo test9Mock Test - Electronics and Communication Engineering ECClick here to start the demo test10Mock Test - Electrical Engineering EEClick here to start the demo test11Mock Test - Ecology and Evolution EYClick here to start the demo test12Mock Test - Geology and Geophysics GGClick here to start the demo test13Mock Test - Instrumentation Engineering INClick here to start the demo test14Mock Test - Mathematics MAClick here to start the demo test15Mock Test - Mechanical Engineering MEClick here to start the demo test16Mock Test - Mining Engineering MNClick here to start the demo test17Mock Test - Metallurgical Engineering MTClick here to start the demo test18Mock Test - Physics PHClick here to start the demo test19Mock Test - Production and Industrial Engineering PIClick here to start the demo test20Mock Test - Textile Engineering and Fibre Science TFClick here to start the demo test21Mock Test - Engineering Sciences XEClick here to start the demo test22Mock Test - Life Sciences XLClick here to start the demo test
Thursday, October 9, 2014
Xenos Great Dane manual or remote central locking- To be secure at all times
There has been a drastic progress in automobile technology over the years; the new discovered techniques are not just restricted to exterior style, engine and infotainment technology. Researchers have devised numerous car lock mechanisms, one product is the Xenos Great Dane manual or remote central locking offered with Nissan Sunny. Xenos Great Dane remote or manual central lock is molded into a trendy piece, it is slender elongated black piece curved on one side, and on it are buttons to lock and open cars and dickey. The lock has a string as well, and can be hung for safety, and there are bits of red patches at the point where the key is strung and on the curved segment.
There has been a drastic progress in automobile technology over the years; the new discovered techniques are not just restricted to exterior style, engine and infotainment technology. Researchers have devised numerous car lock mechanisms, one product is the Xenos Great Dane manual or remote central locking offered with Nissan Sunny. Xenos Great Dane remote or manual central lock is molded into a trendy piece, it is slender elongated black piece curved on one side, and on it are buttons to lock and open cars and dickey. The lock has a string as well, and can be hung for safety, and there are bits of red patches at the point where the key is strung and on the curved segment.

Remote control central locks have become common, and most cars today have remote control lock facilities. The main trigger for advancements in car lock systems is the increase in theft rates caused by increase in population which had led to a highly competitive work atmosphere. With remote locks doors and dickeys can be opened with just a click of button. This becomes more convenient than manual locks where car owners will have to spot the lock hole and turn the key.
The Xenos Great Dane remote or manual central lock will ensure that your car is safe at all times. The lock buttons are on the remote itself, but there are circumstances when people forget to lock cars. The risk of car theft is now on the rise, but if the Xenos Great Dane remote lock is safe with the owner, than the stolen car can still be traced through a computerized machine where each remote lock is encrypted with digital code.
With high tech central remote lock like Xenos Great Dane, occupants will feel a sense of security. Theft incidents all over the world are not restricted to night times, but day thefts have become common, with remote locks it is tough for thieves to gain access into the car. With manual locks, there would have been many duplicate keys to have easy access into cars.
To provide an overview of the features of Xenos Great Dane remote or manual central lock. There are operations tucked into a small piece, the lock has a water resistant control unit, water resistant remote, low current consumption, easy installation, vehicle immobilizer, electronic shock sensor adjustment, shock sensor, electronic learn remote, panic mode, disarm or arm chirps, flash light indication, vehicle locate and remote start.
Automobile technology has transformed to new boundaries over the years, the phrase remote locks was not very common even twenty years ago. Car thefts are on the rise, and there are times when thieves enter the car to steal money and expensive ornaments. All these ugly incidences are wiped out with powerful remote locks like Xenos Great Dane central lock. Apart from being a safe and highly advanced software product, Xenos Great Dane central lock is water resistant, and this wipes away the stress factor completely. When a jar of water flown on to the lock, the central lock is still as powerful as when originally brought. It costs Rs 1,097.
Sensitivity settings
There has been a drastic progress in automobile technology over the years; the new discovered techniques are not just restricted to exterior style, engine and infotainment technology. Researchers have devised numerous car lock mechanisms, one product is the Xenos Great Dane manual or remote central locking offered with Nissan Sunny. Xenos Great Dane remote or manual central lock is molded into a trendy piece, it is slender elongated black piece curved on one side, and on it are buttons to lock and open cars and dickey. The lock has a string as well, and can be hung for safety, and there are bits of red patches at the point where the key is strung and on the curved segment.

Remote control central locks have become common, and most cars today have remote control lock facilities. The main trigger for advancements in car lock systems is the increase in theft rates caused by increase in population which had led to a highly competitive work atmosphere. With remote locks doors and dickeys can be opened with just a click of button. This becomes more convenient than manual locks where car owners will have to spot the lock hole and turn the key.
The Xenos Great Dane remote or manual central lock will ensure that your car is safe at all times. The lock buttons are on the remote itself, but there are circumstances when people forget to lock cars. The risk of car theft is now on the rise, but if the Xenos Great Dane remote lock is safe with the owner, than the stolen car can still be traced through a computerized machine where each remote lock is encrypted with digital code.
With high tech central remote lock like Xenos Great Dane, occupants will feel a sense of security. Theft incidents all over the world are not restricted to night times, but day thefts have become common, with remote locks it is tough for thieves to gain access into the car. With manual locks, there would have been many duplicate keys to have easy access into cars.
To provide an overview of the features of Xenos Great Dane remote or manual central lock. There are operations tucked into a small piece, the lock has a water resistant control unit, water resistant remote, low current consumption, easy installation, vehicle immobilizer, electronic shock sensor adjustment, shock sensor, electronic learn remote, panic mode, disarm or arm chirps, flash light indication, vehicle locate and remote start.
Automobile technology has transformed to new boundaries over the years, the phrase remote locks was not very common even twenty years ago. Car thefts are on the rise, and there are times when thieves enter the car to steal money and expensive ornaments. All these ugly incidences are wiped out with powerful remote locks like Xenos Great Dane central lock. Apart from being a safe and highly advanced software product, Xenos Great Dane central lock is water resistant, and this wipes away the stress factor completely. When a jar of water flown on to the lock, the central lock is still as powerful as when originally brought. It costs Rs 1,097.
Sensitivity settings
Friday, September 19, 2014
Common Light Levels
Common Light Levels Outdoor
Common light levels outdoor at day and night can be found in the table below:| Condition | Illumination | |
| (ftcd) | (lux) | |
| Sunlight | 10,000 | 107,527 |
| Full Daylight | 1,000 | 10,752 |
| Overcast Day | 100 | 1,075 |
| Very Dark Day | 10 | 107 |
| Twilight | 1 | 10.8 |
| Deep Twilight | .1 | 1.08 |
| Full Moon | .01 | .108 |
| Quarter Moon | .001 | .0108 |
| Starlight | .0001 | .0011 |
| Overcast Night | .00001 | .0001 |
Common and Recommended Light Levels Indoor
The outdoor light level is approximately 10,000 lux on a clear day. In the building, in the area closest to windows, the light level may be reduced to approximately 1,000 lux. In the middle area its may be as low as 25 - 50 lux. Additional lighting equipment is often necessary to compensate the low levels.Earlier it was common with light levels in the range 100 - 300 lux for normal activities. Today the light level is more common in the range 500 - 1000 lux - depending on activity. For precision and detailed works, the light level may even approach 1500 - 2000 lux.
The table below is a guidance for recommended light level in different work spaces:
| Activity | Illumination (lux, lumen/m2) |
| Public areas with dark surroundings | 20 - 50 |
| Simple orientation for short visits | 50 - 100 |
| Working areas where visual tasks are only occasionally performed | 100 - 150 |
| Warehouses, Homes, Theaters, Archives | 150 |
| Easy Office Work, Classes | 250 |
| Normal Office Work, PC Work, Study Library, Groceries, Show Rooms, Laboratories | 500 |
| Supermarkets, Mechanical Workshops, Office Landscapes | 750 |
| Normal Drawing Work, Detailed Mechanical Workshops, Operation Theatres | 1,000 |
| Detailed Drawing Work, Very Detailed Mechanical Works | 1500 - 2000 |
| Performance of visual tasks of low contrast and very small size for prolonged periods of time | 2000 - 5000 |
| Performance of very prolonged and exacting visual tasks | 5000 - 10000 |
| Performance of very special visual tasks of extremely low contrast and small size | 10000 - 20000 |
Calculating Illumination
Illumination can be calculated as
I = Ll Cu LLF / Al (1)
where
I = illumination (lux, lumen/m2)
Ll = lumens per lamp (lumen)
Cu = coefficient of utilization
LLF = light loss factor
Al = area per lamp (m2)
Example - Illumination
10 incandencent lamps of 500 W (10600 lumens per lamp) are used in an area of 50 m2. With Cu = 0.6 and LLF = 0.8 illumination can be calculated as
I = 10 (10600 lumens) (0.6) (0.8) / (50 m2)
= 1018 lux
Thursday, September 18, 2014
PSUs considering GATE scores for entry level Engineer positions
Public Sector undertaking (PSU) is a
Government owned corporation or a company in which Central or State
Government have more than 51% share. Basically these Government
companies run like private companies and share profits to Government. A
career with PSU requires, a strong and in-depth technical knowledge and
understanding of core engineering Principals. GATE is one such exam,
where ones technical and general aptitude is tested. Today, more than
2000 jobs are available for a fresh graduate in engineering in major
PSUs in India. The list includes IOCL BHEL, NTPC, BPCL, CEL Power Grid
and likes.
All these Public sector companies
recruit Engineer Trainee (ET) based on the GATE scores. Initially they
would shortlist candidates based on GATE scores and then the process is
followed by GD and Interview for assessment of different facets of
knowledge.
| Logos | Date of starting | Number of vacancies | Streams Eligible | CTC | Links | |
Power grid |
NA | NA | EE | NA | Click here for more details | |
 IOCL |
NA | NA | CH ,CE, CS, EE, EC, ME, IN | NA | Click here for more details | |
 BPCL |
NA | NA | ME, EE, IN, CE, CH | 10.5lakhs PA | Click here for more details | |
 CEL |
NA | NA | EC, EE, ME | NA | Click here for more details | |
 COAL |
NA | NA | ME, EE, GG ,IN | NA | Click here for more details | |
 ONGC |
NA | 745 | NA | NA | Click here for more details | |
HPCL |
Start of online application December 18, 2014Last date for submission of application: February 2, 2015 |
NA | ME, CE, EC, EE, IN, CH | NA | Click here to for more details | |
 MDL |
Start of online application December, 2014Last date for submission of application: January, 2015 |
34 | ME, EE | NA | Click here for more details | |
NTPC |
Last date for submission of application by candidates to NPCCL: February 28, 2015 | NA | CE | NA | Link will be provided soon | |
 PAPCL |
NA | NA | EE, ME, CE, EC, IN, CS | NA | Click here to for more details | |
 THDC |
NA | NA | NA | NA | Click here to for more details |
NHPC
Thursday, July 3, 2014
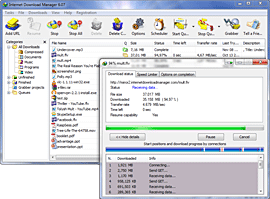
Download Internet Download Manager 7.1 Latest(IDM 7.1) Full Free
Internet Download Manager (IDM) 7.1 is actually a device to improve down load rates of speed by as much as Five times, continue as well as plan downloading.
Version 7.1 provides Windows 8
suitability, provides IDM down load screen with regard to web-players
which you can use in order to down load adobe flash movies through
websites such as YouTube, MySpaceTV, as well as Google Videos.
Additionally, it functions total Windows 7 and Vista assistance, YouTube
grabber, redeveloped scheduler, as well as MMS standard protocol
assistance. The brand new edition furthermore provides enhanced
utilization with regard to Internet explorer 10 and Internet explorer
dependent web browsers, refurbished as well as improved down load
engine, the main superior integration in to almost all most recent web
browsers, enhanced toolbar, along with a useful some other enhancements
as well as new features.
Download Click here
Password: allshare-zone.blogspot.com
Extensive fault restoration
as well as continue capacity will certainly reboot damaged or even
disrupted downloading because of dropped internet connections, system
issues, pc shutdowns, or even unforeseen electricity failures. Easy
visual interface helps make IDM easy to use and simple to make use
of.Internet Download Manager features a intelligent down load reasoning
ignition which includes smart powerful document segmentation as well as
secure multipart downloading engineering in order to speed up your
personal downloading. In contrast to additional down load managers as
well as accelerators Internet Download Manager divides saved data
effectively throughout down load procedure as well as reuses accessible
cable connections without having extra link as well as sign in phases to
attain greatest speed overall performance.
Internet Download Manager
facilitates web proxy hosts, file transfer protocol as well as http
practices, firewalls, redirects, cookies, documentation, MP3 FORMAT
sound as well as MPEG movie content material running. IDM combines
effortlessly in to Ms Internet Explorer, Netscape, WINDOWS LIVE
MESSENGER Explorer, AMERICA ONLINE, Opera, Mozilla, Firefox, Mozilla
Firebird, Avant Web browser, MyIE2, and all sorts of well-known web
browsers in order to instantly manage your own downloading. You may also
drag-n-drop data, or utilize Internet Download Manager through command
line. Internet Download Manager may dial your own modem in the arranged
period, down load the documents you would like, after that say goodbye
and even turn off your pc when it is completed.
Some other functions consist of
multi-lingual assistance, zip preview, down load groups, scheduler
professional, sounds upon various occasions, HTTPS assistance, queue
cpu, html assist as well as guide, improved malware safety upon down
load finalization, intensifying downloading along with quotas (helpful
for connections involving some type of reasonable accessibility plan or
even FAP such as Direcway, Immediate PERSONAL COMPUTER, Hughes, and so
on.), pre-installed down load accelerator, and many more.
Download Click here
Password: allshare-zone.blogspot.com
25 Things I Learned About Life By Age 25
When I turned 25, I
wrote down some of the things I've learned over my short time on earth. The
last year has been a crazy roller-coaster ride which has enabled me to see
certain things like never before.Last year during this time, I was working at
what I would consider my "dream job" — well, before I discovered my
current "job" (I don't think I can even call it a job).
Over the last year, I've tried to
learn from people who have "made it" in life — entrepreneurs,
figureheads, lawyers, bankers and even politicians. I've realized that there is
no formula to success in life, but there are definitely lessons that can be
learned to help along the journey. I came up with the following list which I
hope to someday come back to — but for now, I think it's a pretty accurate
depiction of how I think. So without further adieu:
1. Take risks when you're young. The older you become, the harder it gets. But they should
always be calculated.
2. The most important thing you
learn in school is how to learn.
Once you master that, nothing will stand in your way. Never stop learning.
Wednesday, July 2, 2014
How to check AA/AAA alkaline battery using a Multimeter
We
all run into a situation when batteries in our remotes, toys,
keyboards/mice run out. If we don't know how to check a battery we might
throw out a perfectly fine battery (especially when we have a pile of
them somewhere in the drawer).
This electronics tip has to deal with checking common alkaline AA/AAA batteries or AA/AAA rechargeable batteries for proper voltage with a voltmeter.
Disclaimer : some people might say that a battery should always be tested under load but I have found that in most common household applications this is insignificant and will not change the results of the testing too much.
Things that you will need :
+ Multimeter/Voltmeter
+ Alkaline battery
Basic facts :
The proper voltage for AA/AAA alkaline battery is 1.5V
The proper voltage for AA/AAA NiCd/NiMh rechargeable battery is 1.25 Volts
This electronics tip has to deal with checking common alkaline AA/AAA batteries or AA/AAA rechargeable batteries for proper voltage with a voltmeter.
Disclaimer : some people might say that a battery should always be tested under load but I have found that in most common household applications this is insignificant and will not change the results of the testing too much.
Things that you will need :
+ Multimeter/Voltmeter
+ Alkaline battery
Basic facts :
The proper voltage for AA/AAA alkaline battery is 1.5V
The proper voltage for AA/AAA NiCd/NiMh rechargeable battery is 1.25 Volts
Saturday, June 28, 2014
Thursday, May 15, 2014
Understanding of Railway availiability figures
Understanding availability figures
When you finally get down to booking tickets, you will probably encounter several puzzling availability figures online. After all, finding out that your train and class is "PQWL5/WL5" for the 8th of December isn't very illuminating - what do these figures mean? Worry not, help is at hand in the form of this tutorial.There are several different websites you can use to get availability stats for trains, and this tutorial is especially applicable to these four:
- The official Indianrail website,
- Erail,
- India Rail Info, and
- IRCTC
All screenshots from this tutorial are from Erail, and this tutorial assumes you already know how to read (though not interpret) availability figures displayed on the four sites mentioned earlier. If not, you can always recap at this link.
[a] Figures like AVAILABLE 75
When seats or berths are available in your train/class, it is fairly simple to understand them. The AVAILABLE means that seats/berths are available (duh), and the number following the AVAILABLE tells you exactly how many seats/berths are available. Look at the image below:

Screenshot from www.erail.in
In this case, should I want to travel by First AC (1A) on the 21st of October, I don't have to worry too much as 75 seats are available at the moment.
[b] Figures like RAC87/RAC 74
On trains with sleeping accommodation, after all confirmed berths have been sold out, passengers are usually placed on an RAC ("Reservation Against Cancellation") list. Being on the RAC list guarantees you a place on the train, with a small catch - you are guaranteed only a seat on the train. If enough passengers cancel, you will be allotted a sleeping-berth.
The following image is one for a train-class-date combination that has now reached the RAC list:

Screenshot from www.erail.in
So if I decide to travel by Sleeper Class (SL) on this train on the 8th of November, I will be placed on the RAC list.
Hold on, you might say. Why are there two sets of numbers? Why is it RAC87/RAC 74, and what position on the RAC list will you get - 87 or 74? Good questions. The first number indicates the serial waitlist or RAC position; the second, the running waitlist or RAC position. I suspect this clears nothing up for you; I'll simplify it a bit more.
The serial number (the first of the two) indicates your position in the queue since the waitlist/RAC list started, and your serial number will never change. So in this case, all confirmed berths have been sold out, and you are the 87th person to join the queue after the RAC list started. The second number (the running waitlist/RAC list number) is more important - it denotes the position you currently are at in the waitlist or RAC list. As and when people cancel their tickets, your running waitlist/RAC list number will reduce until your ticket gets confirmed (if that happens). So the first number denotes the position you would have been at in the waitlist/RAC list had no cancellations occurred. So in this case, you would have been RAC87, but as 13 people have cancelled their tickets since the RAC list started, you will be RAC 74 if you book a ticket now.
So why two numbers, you might ask. Why not just keep the running waitlist number and avoid all confusion? Well, having two numbers does serve a purpose. For many passengers who cannot access the net or use technology to find out which coach and berth they've finally been allotted, the only way to check before boarding the train is to look at the charts pasted at the station. Checking your serial waitlist number on the list is easy - only one person can have a serial RAC position of 87, so all s/he needs to do is look for that entry in the chart. On the other hand, many people will have the running RAC position of 74 at different times, which makes searching for the entry on the chart significantly more difficult.
Another use of two numbers is that before making your booking, you can:
- tell how many passengers have already cancelled their tickets,
- look at cancellation trends for your train and class, which will help you predict its chances of confirmation with greater accuracy.
Availability figures like the one seen below for AC Chair Car (CC) on the 1st of October can seem even more perplexing:

Screenshot from www.erail.in
You now (hopefully) recognise the two numbers - the first (16) is the serial position; the second (4), the running position. But what do GNWL and WL mean?
Four-letter words (not that four-letter word!) when checking availability usually suggest that a waitlist has started. In trains with sleeping accommodation, the order is usually as follows:
- If confirmed berths are available, you will be allotted one.
- Once all confirmed berths have been sold, you will be placed on the RAC list.
- Once all confirmed berths and RAC positions booked, you will be placed on the waitlist.
Back to the example above, the first word tells you that it is a waitlist as well as the type of waitlist. Here are the types of waitlists you might encounter:
- GNWL (General Waitlist),
- CKWL (Tatkal Waitlist),
- RLWL (Remote Location Waitlist, also abbreviated RLGN),
- PQWL (Pooled Quota Waitlist),
- RSWL (Roadside Waitlist)
Quotas like the foreign tourist quota, the ladies quota, the senior citizen quota, the defence quota and the physically handicapped quota have no waitlists. Once all confirmed seats or berths have been sold from these quotas, the status changes directly to NOT AVAILABLE.
To wrap up this example, if you book this ticket, you will be 4th on the (general) waitlist. Expecting four cancellations from other passengers is not too unreasonable in this case, and this ticket will probably get confirmed.
[d] Figures like REGRET/WL300
If I wanted to buy a ticket in Sleeper Class (SL) on this train for the 3rd of November, I wouldn't get very far.

Screenshot from www.erail.in
If you see REGRET as an availability status while trying to book tickets, you're going to have to choose another train or class. REGRET means that the train-class-date combination is so full that they've stopped issuing tickets even on the waitlist. In short, the railways know there is no chance that such a high waitlist will get confirmed, so they're telling you to take your business elsewhere.
[e] Figures like GNWL/AVAILABLE
This is a slightly strange figure to see. The first word suggests a waitlist, so why is there an AVAILABLE after that?
(First AC, 14th October)

Screenshot from www.erail.in
When you see WL/AVAILABLE (irrespective of what type of waitlist it is), it means that at least one seat or berth is available. This status tells you that the train got full, and hence a waitlist was started, but due to cancellations, seats or berths are now available. Annoyingly, it doesn't tell you exactly how many seats or berths are available, so the only assumption you can make is that one seat or berth is available. Only after booking will you know for sure.
If you see WL/AVAILABLE for a train-class combination over a series of dates, it's probably because the railways have decided to add extra coaches of that class to the train - the resulting capacity expansion killing any waitlists.
Alright, that's all folks!
Saturday, March 29, 2014
GATE 2015 EE Syllabus
|
1.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING – EE
|
|
Engineering Mathematics
|
|
|
|
Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systems of linear equations, Eigen values
and eigen vectors.
Calculus: Mean value theorems, Theorems of integral calculus, Evaluation of definite and improper integrals, Partial Derivatives, Maxima and minima, Multiple integrals, Fourier series. Vector identities, Directional derivatives, Line, Surface and Volume integrals, Stokes, Gauss and Green's theorems. Differential equations: First order equation (linear and nonlinear), Higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients, Method of variation of parameters, Cauchy's and Euler's equations, Initial and boundary value problems, Partial Differential Equations and variable separable method. Complex variables: Analytic functions, Cauchy's integral theorem and integral formula, Taylor's and Laurent' series, Residue theorem, solution integrals. Probability and Statistics: Sampling theorems, Conditional probability, Mean, median, mode and standard deviation, Random variables, Discrete and continuous distributions, Poisson, Normal and Binomial distribution, Correlation and regression analysis. Numerical Methods: Solutions of non-linear algebraic equations, single and multi-step methods for differential equations. Transform Theory: Fourier transform, Laplace transform, Z-transform. |
|
|
|
GENERAL APTITUDE(GA):
|
|
Verbal Ability: English grammar, sentence completion, verbal analogies,
word groups, instructions, critical reasoning and verbal deduction.
|
|
|
|
Electrical Engineering
|
|
Electric Circuits and Fields: Network graph, KCL, KVL, node and mesh analysis,
transient response of dc and ac networks; sinusoidal steady-state analysis,
resonance, basic filter concepts; ideal current and voltage sources,
Thevenin's, Norton's and Superposition and Maximum Power Transfer theorems,
two-port networks, three phase circuits; Gauss Theorem, electric field and
potential due to point, line, plane and spherical charge distributions;
Ampere's and Biot-Savart's laws; inductance; dielectrics; capacitance.
Signals and Systems: Representation of continuous and discrete-time signals; shifting and scaling operations; linear, time-invariant and causal systems; Fourier series representation of continuous periodic signals; sampling theorem; Fourier, Laplace and Z transforms. Electrical Machines: Single phase transformer - equivalent circuit, phasor diagram, tests, regulation and efficiency; three phase transformers - connections, parallel operation; auto-transformer; energy conversion principles; DC machines - types, windings, generator characteristics, armature reaction and commutation, starting and speed control of motors; three phase induction motors - principles, types, performance characteristics, starting and speed control; single phase induction motors; synchronous machines - performance, regulation and parallel operation of generators, motor starting, characteristics and applications; servo and stepper motors. Power Systems: Basic power generation concepts; transmission line models and performance; cable performance, insulation; corona and radio interference; distribution systems; per-unit quantities; bus impedance and admittance matrices; load flow; voltage control; power factor correction; economic operation; symmetrical components; fault analysis; principles of over-current, differential and distance protection; solid state relays and digital protection; circuit breakers; system stability concepts, swing curves and equal area criterion; HVDC transmission and FACTS concepts. Control Systems: Principles of feedback; transfer function; block diagrams; steady-state errors; Routh and Niquist techniques; Bode plots; root loci; lag, lead and lead-lag compensation; state space model; state transition matrix, controllability and observability. Electrical and Electronic Measurements: Bridges and potentiometers; PMMC, moving iron, dynamometer and induction type instruments; measurement of voltage, current, power, energy and power factor; instrument transformers; digital voltmeters and multimeters; phase, time and frequency measurement; Q-meters; oscilloscopes; potentiometric recorders; error analysis. Analog and Digital Electronics: Characteristics of diodes, BJT, FET; amplifiers - biasing, equivalent circuit and frequency response; oscillators and feedback amplifiers; operational amplifiers - characteristics and applications; simple active filters; VCOs and timers; combinational and sequential logic circuits; multiplexer; Schmitt trigger; multi-vibrators; sample and hold circuits; A/D and D/A converters; 8-bit microprocessor basics, architecture, programming and interfacing. Power Electronics and Drives: Semiconductor power diodes, transistors, thyristors, triacs, GTOs, MOSFETs and IGBTs - static characteristics and principles of operation; triggering circuits; phase control rectifiers; bridge converters - fully controlled and half controlled; principles of choppers and inverters; basis concepts of adjustable speed dc and ac drives. |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)